Search
Journal of Agricultural Big Data ›› 2025, Vol. 7 ›› Issue (2): 161-172.doi: 10.19788/j.issn.2096-6369.000098
Previous Articles Next Articles
QIAN Tao1,2,3,4( ), ZHAN YaTing5,6,7, LI Yin5,6,7, SONG Ke5,6,7, SHAO MingChao1,2,3,4, YU ZhongZhi1,2,3,4, CHENG Tao1,2,3,4, YAO Xia1,2,3,4, ZHENG HengBiao1,2,3,4, ZHU Yan1,2,3,4,7, CAO WeiXing1,2,3,4, JIANG ChongYa1,2,3,4,7,*(
), ZHAN YaTing5,6,7, LI Yin5,6,7, SONG Ke5,6,7, SHAO MingChao1,2,3,4, YU ZhongZhi1,2,3,4, CHENG Tao1,2,3,4, YAO Xia1,2,3,4, ZHENG HengBiao1,2,3,4, ZHU Yan1,2,3,4,7, CAO WeiXing1,2,3,4, JIANG ChongYa1,2,3,4,7,*( )
)
Received:2025-01-28
Accepted:2025-03-19
Online:2025-06-26
Published:2025-06-23
Contact:
JIANG ChongYa
QIAN Tao, ZHAN YaTing, LI Yin, SONG Ke, SHAO MingChao, YU ZhongZhi, CHENG Tao, YAO Xia, ZHENG HengBiao, ZHU Yan, CAO WeiXing, JIANG ChongYa. Crop Classification Research Based on Vehicle Images and HLS Time-series Remote Sensing Data[J].Journal of Agricultural Big Data, 2025, 7(2): 161-172.
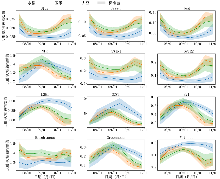
Fig. 4
Spectral curves of different crops. The solid line represents the mean of ground samples, and the shaded area indicates the standard deviation. Reflectance for each date is the average of the previous 15 days. For example, the reflectance on 08/01 is the average from July 16 to July 31."

Table 3
Classification accuracy of different models"
| 类别 | SVM | RF | CNN | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UA (%) | PA (%) | F1-score | UA (%) | PA (%) | F1-score | UA (%) | PA (%) | F1-score | |
| 水稻 | 78.52 | 83.46 | 0.81 | 94.53 | 95.28 | 0.95 | 82.31 | 95.28 | 0.89 |
| 玉米 | 59.69 | 82.80 | 0.69 | 84.52 | 76.34 | 0.80 | 75.49 | 82.80 | 0.79 |
| 大豆 | 72.73 | 49.23 | 0.59 | 74.24 | 75.38 | 0.75 | 85.71 | 36.92 | 0.52 |
| 其他 | 94.27 | 82.22 | 0.88 | 92.51 | 96.11 | 0.94 | 92.55 | 96.67 | 0.95 |
| 总体精度 OA (%) | 78.06 | 89.03 | 85.16 | ||||||
| Kappa系数 | 0.69 | 0.85 | 0.79 | ||||||
| [1] |
黄翀, 侯相君. 基于Bi-LSTM模型的时间序列遥感作物分类研究. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(21): 4144-4157.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2022.21.005 |
| [2] | 赵龙才, 李粉玲, 常庆瑞. 农作物遥感识别与单产估算研究综述. 农业机械学报, 2023, 54(2): 1-19. |
| [3] | YI Z, JIA L, CHEN Q. Crop classification using Multi-temporal Sentinel-2 Data in the Shiyang River Basin of China. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(24): 4052. |
| [4] | LUO K, LU L, XIE Y, et al. Crop type mapping in the central part of the North China Plain using Sentinel-2 time series and machine learning. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2023, 205: 107577. |
| [5] | LI J, LEI H. Tracking the spatio-temporal change of planting area of winter wheat-summer maize cropping system in the North China Plain during 2001-2018. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2021, 187: 106222. |
| [6] | YAN Y, RYU Y. Exploring Google Street View with deep learning for crop type mapping. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2021, 171: 278-296. |
| [7] | WU F, WU B, ZHANG M, et al. Identification of crop type in crowdsourced road view photos with Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors, 2021, 21(4): 1165. |
| [8] | JIANG C, GUAN K, HUANG Y, et al. A vehicle imaging approach to acquire ground truth data for upscaling to satellite data: A case study for estimating harvesting dates. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2024, 300: 113894. |
| [9] | PALIYAM M, NAKALEMBE C, LIU K, et al. Street2sat: A machine learning pipeline for generating ground-truth geo-referenced labeled datasets from street-level images[C]. ICML 2021 Workshop on Tackling Climate Change with Machine Learning. 2021. |
| [10] | PILGER N, BERG A, JOOSSE P. Semi-automated roadside image data collection for characterization of agricultural land management practices. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(14): 2342. |
| [11] | JIA D, GAO P, CHENG C, et al. Multiple-feature-driven co-training method for crop mapping based on remote sensing time series imagery. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 41(20): 8096-8120. |
| [12] | TIAN X, CHEN Z, LI Y, et al. Crop classification in mountainous areas using Object-oriented methods and multi-source data: A case study of Xishui County, China. Agronomy, 2023, 13(12): 3037. |
| [13] | CLAVERIE M, JU J, MASEK J G, et al. The Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 surface reflectance data set. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2018, 219: 145-161. |
| [14] | LI B, TI C, YAN X. Estimating rice paddy areas in China using multi-temporal cloud-free normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) imagery based on change detection. Pedosphere, 2020, 30(6): 734-746. |
| [15] | JONSSON P, EKLUNDH L. Seasonality extraction by function fitting to time-series of satellite sensor data. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(8): 1824-1832. |
| [16] | LIANG J, REN C, LI Y, et al. Using Enhanced Gap-Filling and Whittaker Smoothing to Reconstruct High Spatiotemporal Resolution NDVI Time Series Based on Landsat 8, Sentinel-2, and MODIS Imagery. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2023, 12(6): 214. |
| [17] | WU G, JIANG C, KIMM H, et al. Difference in seasonal peak timing of soybean far-red SIF and GPP explained by canopy structure and chlorophyll content. Remote sensing of environment, 2022, 279: 113104. |
| [18] | BREIMAN L. Random forests. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1): 5-32. |
| [19] | WANG S, AZZARI G, LOBELL D B. Crop type mapping without field-level labels: Random forest transfer and unsupervised clustering techniques. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2019, 222: 303-317. |
| [20] | LI H, SONG X P, HANSEN M C, et al. Development of a 10-m resolution maize and soybean map over China: Matching satellite- based crop classification with sample-based area estimation. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2023, 294: 113623. |
| [21] | XU J, CHEN C, ZHOU S, et al. Land use classification in mine- agriculture compound area based on multi-feature random forest: A case study of Peixian. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 2024, 7: 1335292. |
| [22] | CHAWLA N V, BOWYER K W, HALL L O, et al. SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2002, 16: 321-357. |
| [23] | DOUZAS G, BACAO F, FONSECA J, et al. Imbalanced learning in land cover classification: Improving minority classes’ prediction accuracy using the geometric SMOTE algorithm. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(24): 3040. |
| [24] | 张馨予, 蔡志文, 杨靖雅, 等. 时序滤波对农作物遥感识别的影响. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(4): 215-224. |
| [25] | HUETE A, DIDAN K, MIURA T, et al. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2002, 83(1-2): 195-213. |
| [26] | XIAO X, ZHANG Q, HOLLINGER D, et al. Modeling gross primary production of an evergreen needleleaf forest using MODIS and climate data. Ecological Applications, 2005, 15(3): 954-969. |
| [27] | GITELSON A A, KAUFMAN Y J, STARK R, et al. Novel algorithms for remote estimation of vegetation fraction. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2002, 80(1): 76-87. |
| [28] | ZHAI Y, ROY D P, MARTINS V S, et al. Conterminous United States Landsat-8 top of atmosphere and surface reflectance tasseled cap transformation coefficients. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2022, 274: 112992. |
| [29] | 熊曦柳, 胡月明, 文宁, 等. 耕地遥感识别研究进展与展望. 农业资源与环境学报, 2020, 37(6): 856-865. |
| [30] | ORYNBAIKYZY A, GESSNER U, MACK B, et al. Crop type classification using fusion of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data: Assessing the impact of feature selection, optical data availability, and parcel sizes on the accuracies. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(17): 2779. |
| [31] | 何真, 胡洁, 蔡志文, 等. 协同多时相国产GF-1和GF-6卫星影像的艾草遥感识别. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(1): 186-195. |
| [32] | JIN M, WANG P, LI Y. HyA-GAN: Remote sensing image cloud removal based on hybrid attention generation adversarial network. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 45(6): 1755-1773. |
| [33] | WEI P, YE H, QIAO S, et al. Early crop mapping based on Sentinel-2 time-series data and the random forest algorithm. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(13): 3212. |
| [34] | WANG S, DI TOMMASO S, FAULKNER J, et al. Mapping crop types in southeast India with smartphone crowdsourcing and deep learning. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(18): 2957. |
| [35] | SÁNCHEZ A, NANCLARES R, PELAGIO U, et al. Agave crop segmentation and maturity classification with deep learning data- centric strategies using very high-resolution satellite imagery. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2023, 44(22): 7017-7032. |
| [1] | ZHANG DanDan, ZHAO RuiXue, KOU YuanTao, XIAN GuoJian. Crop Trait Regulating-genes Knowledge Graph Datasets [J]. Journal of Agricultural Big Data, 2025, 7(2): 220-226. |
| [2] | GAO ZhuoJun, ZHANG DanDan, CHEN RongYu. Construction Data Set of Knowledge Map of main Crops Approved Varieties in Guangdong Province from 2016 to 2023 [J]. Journal of Agricultural Big Data, 2025, 7(2): 261-268. |
| [3] | YUE RuiJun, HE Liang, TANG MinRui, YAN Wei, LIU ShengQuan, YANG WanXia, SUN WeiHong, HUANG YongFeng. Agri-CBI: Agricultural Big Data Security Governance Model Leveraging Cloud-Blockchain Integration [J]. Journal of Agricultural Big Data, 2024, 6(3): 333-350. |
| [4] | WU YunKun, YANG Ying, LI Hao, XIONG Jian, CHEN XiangLing. Exploration of Big Data Security Issues in the Field of Intelligent Agriculture [J]. Journal of Agricultural Big Data, 2024, 6(3): 380-391. |
| [5] | Ling Zhang, Yingying Zhang, Aili Shi, Ran Zheng, Ting Zhang. A Dataset of Coccinellids in Longhua, Chengde, Hebei Province from 2018 to 2021 [J]. Journal of Agricultural Big Data, 2022, 4(4): 24-32. |
| [6] | Yun Tao, Xiefeng Cheng. Comparative Study on Regional Big Data Development and Regional Agricultural Big Data Construction Level [J]. Journal of Agricultural Big Data, 2022, 4(1): 125-135. |
| [7] | Qing Zhao, Guoqiang Li, Feng Hu, Laigang Wang, Hecang Zang, Jie Zhang, Meng Wang, Hui Zhang, Guoqing Zheng. Construction and Application of a Comprehensive Service Platform for Intelligent Field Crop Production [J]. Journal of Agricultural Big Data, 2021, 3(4): 29-39. |
| [8] | Huijuan Wang, Qian Xu, Ailian Zhou, Xiaohe Liang, Nengfu Xie, Xiaoyu Li, Saisai Wu. The Development of Blockchain and Its Application in Agriculture [J]. Journal of Agricultural Big Data, 2021, 3(3): 76-86. |
| [9] | Qiang Li, Maofang Gao, Ying Fang. Research on the Construction of the Agricultural Big Data Information Platform [J]. Journal of Agricultural Big Data, 2021, 3(2): 24-30. |
| [10] | Fuqiao Chen, Chen Ling. Functional Design and Development of the Big Data Center of the Whole Tea Industry Chain [J]. Journal of Agricultural Big Data, 2021, 3(2): 54-66. |
| [11] | Rui Jiang, Fenghong Huang, Yu Wu, Mengjia Huo, Huawei Liu. Big Data Construction of Oil Crops (Rapeseed, Peanut) Whole Industrial Chain [J]. Journal of Agricultural Big Data, 2021, 3(2): 67-74. |
| [12] | Jun Gu, Shuhua Jia, Qinghong Zeng. Research of Construction of the Big Data Platform for Agricultural Single Product across the Whole Industry Value Chain Based on Knowledge Center [J]. Journal of Agricultural Big Data, 2021, 3(1): 25-32. |
| [13] | Jie Zhang, Shengping Liu, Huili Yue, Lü Chunyang, Wei Hong. Construction and Application of Big Data Platform for Intelligent Apiculture [J]. Journal of Agricultural Big Data, 2021, 3(1): 3-13. |
| [14] | Qiuzi Wen‑Han, Yongqiang Zheng, Yang Liu. Research and Application of Citrus Big Data [J]. Journal of Agricultural Big Data, 2021, 3(1): 33-44. |
| [15] | Haiyan Liu, Rong Yang, Tongyu Hou, Wei Zhao, Zhaoqun Yao, Haijiang Wang, Ze Zhang, Pan Gao, Lü Xin. Construction of a Visual Analysis Platform for Microorganism Resources Big Data from Cotton Fields in Xinjiang, China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Big Data, 2021, 3(1): 45-55. |
|
||

